The Data Quality model represents the grounds where the system for assessing the quality of data products is built on. In a Data Quality model, the main Data Quality characteristics that must be taken into account when assessing the properties of the intended data product are established.
The Quality of a Data Product may be understood as the degree to which data satisfy the requirements defined by the product-owner organization. Specifically, those requirements are the ones that are reflected in the Data Quality model through its characteristics (Accuracy, Completeness, Consistency, Credibility, Currentness, Accessibility...).
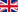
The Data Quality model defined in the standard ISO/IEC 25012 is composed of 15 characteristics, shown in the picture bellow:
The Data Quality characteristics are classified in to main categories:
- Inherent Data Quality: Inherent data quality refers to the degree to which quality characteristics of data have the intrinsic potential to satisfy stated and implied needs when data is used under specified conditions. From the inherent point of view, data quality refers to data itself, in particular to:
- data domain values and possible restrictions (e.g. business rules governing the quality required for the characteristic in a given application);
- relationships of data values (e.g. consistency);
- metadata.
-
System-Dependent Data Quality: System dependent data quality refers to the degree to which data quality is reached and preserved within a computer system when data is used under specified conditions.
From this point of view data quality depends on the technological domain in which data are used; it is achieved by the capabilities of computer systems' components such as: hardware devices (e.g. to make data available or to obtain the required precision), computer system software (e.g. backup software to achieve recoverability), and other software (e.g. migration tools to achieve portability).